Kanadevia Technical Review Vol.86

- 1.Demonstration Test Results and Future Prospects for the Rapid Fiber Filtration System for High-Turbidity Water in Cambodia
- 2.Development of Catamaran-Type Buoys for Miniaturization of Mooring Lines and Considerations of Their Application to Floating Fish Reefs [Japanese]
- 3.Development of Backingless Penetration Bead Welding and Multi-layer Welding Techniques Using Keyhole TIG [Japanese]
- 4.Awareness-Raising Effects of Outreach Programs at Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan [Japanese]
- 5.Fundamental Study on the Development and Social Implementation of a Lithium-Ion Batteries Detection System Utilizing RFID Tag [Japanese]
Short report

Reliable water infrastructure remains a challenge in Southeast Asia's regional cities and rural areas. Kanadevia developed a “Rapid Fiber Filtration System” to treat high-turbidity raw water, and tested it in Cambodia. The system successfully treated water with very high turbidity levels of up to 547 NTU, generating treated water that met local quality standards. Although changes in raw water quality temporarily affected performance, these issues were effectively resolved through appropriate adjustments. Kanadevia plans to improve system responsiveness, optimize operations, and standardize equipment to reduce costs. These efforts are designed to ensure safe water supply and support sustainable development in the region.
- Lead author
- Tetsuro Fujita
- Joint author
- Makoto Fujioka
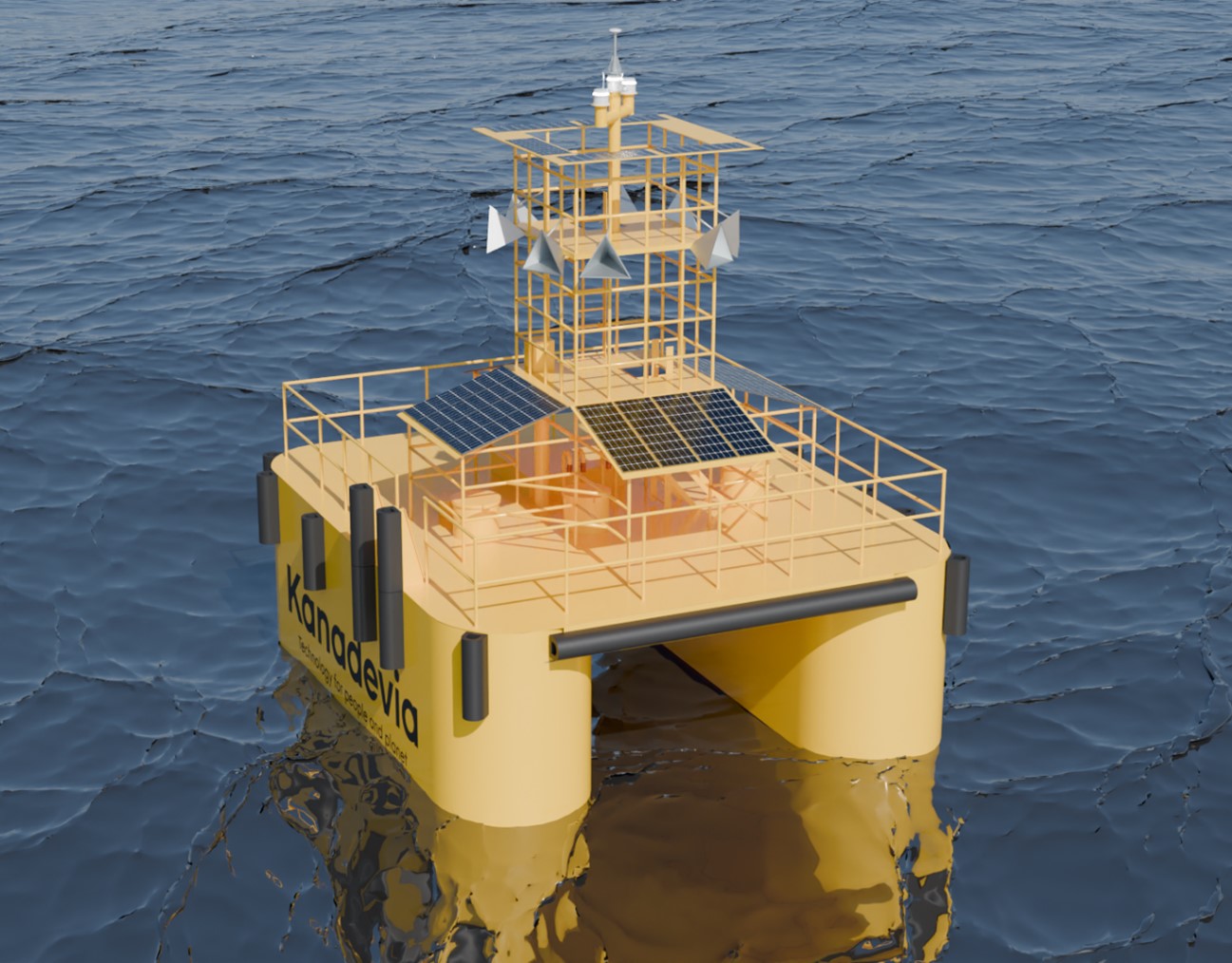

Kanadevia Corporation handles a range of different floating structures, one of which is steel buoys. These buoys are moored in fixed positions at sea with a single mooring line, and their service life is generally ten years. This mooring line is made of chains or wire cables, which, while they are not replaced during the buoy’s service life, are designed to not break even when exposed to wear and corrosion. With these steel buoys, however, greater water depths require longer mooring lines, which increases weight and requires larger floating structures. This requires larger amounts of steel, so Kanadevia has been exploring ways to reduce mooring line size and weight. Consequently, we have developed a catamaran-type buoy that reduces drag from currents and waves on the float, allowing for smaller mooring lines. A catamaran is a type of twin-hulled boat connected by a deck, offering benefits such as reduced drag force from the bow direction and a wide deck area. This report presents some of the development details of these catamaran-type buoys and discusses the effects of using catamaran-type buoys as floating fish reefs.
- Lead author
- Yuki Koga
- Joint author
- Hideyuki Niizato, Yutaka Okamoto, Akihiko Ase,
Yasutaka Hayashi
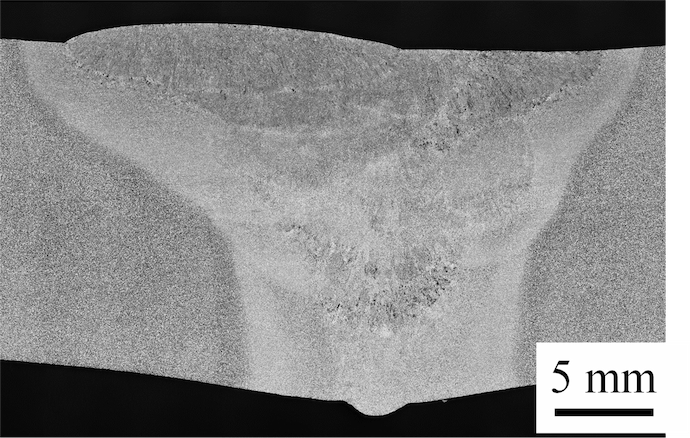
Backingless penetration bead welding does not use backing material for butt joints; rather, after the weld bead is formed on the back side of the welded area in the first layer, the rest is then layered over the top. This method is an effective technique for butt joints that require full penetration welds. However, to prevent weld defects, the amount of heat input and the feeding rate of weldimg consumables must be appropriately controlled according to the root gap, which changes during the welding process. As this requires advanced welding skills, the process is increasingly being automated. In this development, we clarified the scope of the appropriate welding conditions that can be assumed to prevent defects, and established automatic penetration bead welding and multi-layer welding techniques that adapts groove variations during welding. In addition, we conducted a demonstration test with the goal of applying this to the manufacture of penstocks, and demonstrated that the developed technology can achieve sufficient welding quality and reduce the number of processes.
- Lead author
- Yohei Abe

Prior to Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan, Kanadevia Corporation conducted outreach programs for elementary school students as part of the EXPO School Caravan initiative organized by the Secretariat of the Headquarters for the World Expo 2025, Cabinet Secretariat. In these programs, students used remote viewing technology to take virtual field trips to a waste to energy plant’s monitoring facility and presented their predictions about future waste management systems.
This report presents the results of a quantitative text analysis of worksheets collected after the outreach programs, evaluating the effectiveness of the awareness-raising efforts. The analysis revealed that approximately 75% of the students grasped the core message of Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan. Additionally, the programs successfully conveyed the importance of hygienic waste treatment and waste reduction through incineration.
The outreach programs provided by our company served as a valuable opportunity for students to reflect on future society and potentially connect these insights to their future actions.
- Lead author
- Shota Hayashi
- Joint author
- Yosuke Sugiura, Masashi Ushiro,
Seiichiro Yamashita
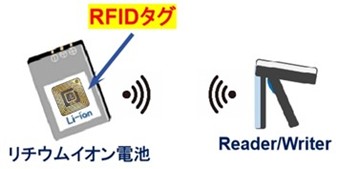
In recent years, fire incidents caused by Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs) have been rapidly increasing at waste collection sites and treatment facilities. Current countermeasures primarily rely on early fire suppression technologies using sensors after ignition, and no technology exists to detect and remove LIBs embedded in waste beforehand. This study aims to establish a detection method for LIBs using RFID tags. In the proposed approach, LIB-containing products are labeled with unidirectional RFID tags, which are then detected by a Reader-Writer (R/W). Experiments first confirmed the effectiveness of the unidirectional tags, demonstrating that LIBs can be detected under typical environmental conditions. Notably, detection performance was found to improve in spaces surrounded by metal. Furthermore, considering future social implementation, detection performance was evaluated at the waste collection stage, including small electronic device collection boxes and waste truck loading inlets. These results confirm that LIBs can be effectively detected, provided that RFID tags are attached in advance.
- Lead author
- Koji Sakakibara
- Joint author
- (Kyushu University) Eriko Aibara,
Hirofumi Nakayama,Kazuki Suehiro,
Haruichi Kanaya,
(Kyushu Environmental Evaluation Association)
Takayuki Shimaoka
Short report
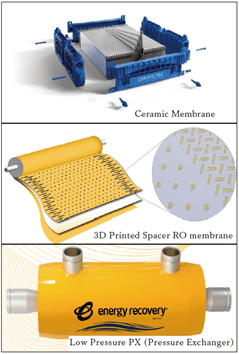
Australia, the driest inhabited continent, faces mounting pressures on water security due to climate change, with increasing variability, droughts, floods, and extreme weather events challenging both municipal and industrial water users. Membrane-based treatment technologies, particularly desalination and purified recycled water (PRW), are increasingly adopted as climate-independent sources of high-quality water. However, these processes are traditionally associated with high energy demand, creating tension with the water industry’s need to decarbonise in line with national Net Zero commitments. In response to this requirement to reduce the energy consumed in water treatment processes, Osmoflo has been investigating, developing and integrating a range of innovative technologies all designed to reduce the specific energy consumption of the treatment process. Specifically, three recent technologies are described herein, which include (1) a ceramic membrane technology, (2) a unique 3D printed spacer RO (Reverse Osmosis) membrane and (3) a Low Pressure Isobaric Pressure Exchange Energy Recovery Device (LPPX). The energy savings of the 3 innovative technologies are evaluated and compared against traditional membrane treatment processes at an operational brewery wastewater facility in Queensland, Australia.
- Keywords
- #Advanced Membrane Technology
#Desalination
#Reverse Osmosis
#Water
#Energy
#Carbon
#Energy Recovery

Kanadevia has developed a zeolite membrane that selectively separates water from organic compounds. We provide a range of users with membrane dehydration equipment that recycles organic solvents or upgrades bioethanol. Recently, we also developed biogas upgrading units to separate carbon dioxide (CO2) from biogas as a new application of zeolite membrane, and completed demonstration tests overseas. Kanadevia’s biogas upgrading units selectively remove CO2 with minimal methane losses, thereby contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and achieving high biomethane recovery.
- Keywords
- #Zeolite membrane
#Biogas upgrading
#GHG reduction
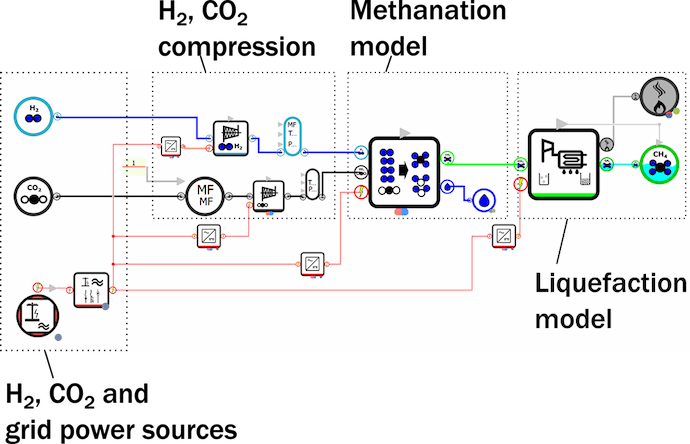
Renewable Gas R&D group at Kanadevia Inova AG (KVI) has been developing a software tool (DSP: Decision Support Platform) for conceptual and early design evaluation and optimization of complex, coupled waste management and energy systems. The tool fully integrates process, economic and environmental / social life cycle analyses. This report gives an overview of the tool design and features, with illustrative examples from application cases executed in KVI and Kanadevia Corporation (KVC). The next phase of the development will focus on expanding the simulation libraries, and user interface enhancements for transfer from R&D environment to wider use in engineering, project development and sales.

Kanadevia Inova AG (KVI) has released to the market the new product Bulky Waste Detection. It has been piloted for more than one year in two Swiss plants and KVI is actively advancing commercial discussions across the European and Middle East Waste-to-Energy (WtE) sector and continues to generate promising new opportunities. The Bulky Waste Detection is a flexible computer vision system that can be installed in new plants or as a retrofit. It monitors 24/7 the tipping of waste and warns the crane operator in real time if a bulky item has entered the bunker through a user-friendly interface. The user receives all the information needed to be able to decide and act, i.e. either shredding, removing or releasing the item depending on its potential problematic impact to plant operation.

Kanadevia already offers a remote monitoring and operations support system that connects to A.I/TEC, or our Remote Monitoring Operation Support Center (ROC) . However, we have also developed a Remote Care System that enables remote monitoring and operations support for incinerators in Japan and overseas that are not connected to the ROC. This system allows operators to adjust the operation of the Automatic Combustion Control System (ACC), monitor furnace operation, and recalibrate various automatic control systems remotely. The Remote Care System has already been deployed at two incineration facilities overseas.
- Keywords
- #Remote monitoring
#Waste incineration
#Operational support
#Data analysis
#Diagnosis support
Click here for inquiries about Kanadevia technology
