Kanadevia Technical Review Vol.85

- 1.Truck Scale Autonomous Driving System for Cashless Transactions to Enhance Operational Speed and Efficiency
- 2.Demonstration of Optimized Collection Routes for Municipal Solid Waste Collection and Transport
- 3.Field Survey of Microplastic Discharge at Wastewater Treatment Facilities
- 4.Basic Design of a New Steel Floating Pier and Verification of its Motion Response Characteristics
- 5.Development of High-Precision Vibration Sensor Suitable for Precise Lissajous Figure Drawing and its Application to Machine Condition Diagnoses
[Short report]

In recent years, payment methods have diversified with the rise of cashless transactions, with cashless adoption promoted by both the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, as well as the establishment of the Digital Agency to advance the digitization of public services. Currently, waste disposal facilities are required to alleviate congestion and enhance operational speed and efficiency. Kanadevia Corporation is working towards cashless solutions for general incoming vehicles and licensed contractors, aiming to reduce congestion for general incoming vehicles and improve resident services, as well as streamline invoice processing. As a result of demonstration tests at the Watagari Clean Center, we successfully implemented two types of cashless payment functions in the Truck Scale Autonomous Driving System.
- Lead author
- Hideharu Tanaka
- Joint author
- Toshikatsu Masuoka, Masanori Yasunaga, Terushi Hirabayashi, Tohru Satoh, Osamu Ohshima, Nobumasa Yoshino, Takuo Satoh
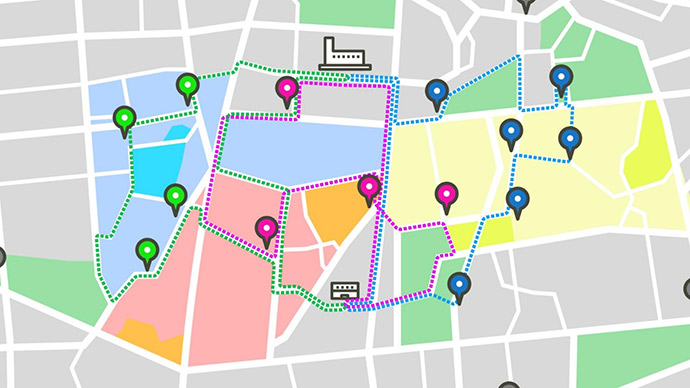
The waste management industry faces labor shortages, and there is a demand for improving the efficiency of collection and transport operations using IoT and AI technologies. While automated dispatching services have been introduced in the logistics industry, adapting them to municipal solid waste collection requires considering unique conditions. Kanadevia Corporation developed a wearable sensor-based waste volume detection system and is implementing AI dispatching services to optimize collection routes. In a demonstration targeting collection in Odawara City, the number of routes was reduced from 14 to 13, and the driving distances were reduced by approximately 73 km (7.1 %). We also received very positive feedback on the optimized route. This demonstration indicated that route optimization using AI technology is effective in reducing driving distances. Furthermore, it was shown that the experience and knowledge of workers contribute to further decreasing driving distances.
- Lead author
- Nanako Ogawa
- Joint author
- Tohru Satoh, Keiichi Iki, Noboru Yamamoto
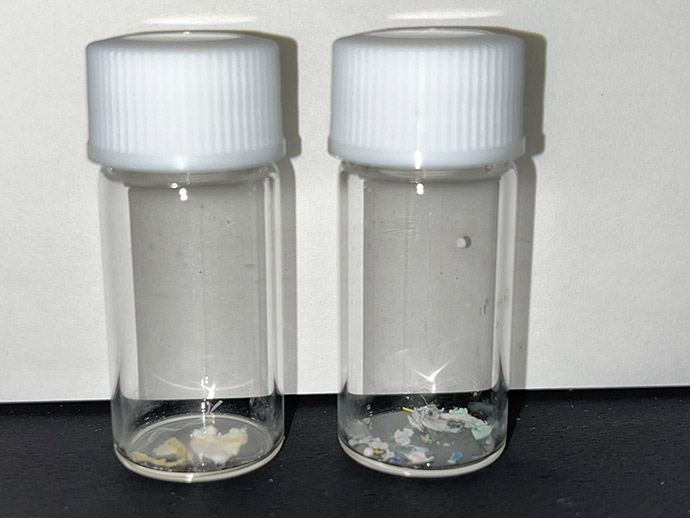

Microplastics are defined as plastics smaller than 5 mm. Because of their small size and ubiquity, there are concerns about the health effects on fish that ingest microplastics, mainly in water, and subsequent bioaccumulation in humans.
Discharged water from wastewater treatment facilities is considered to be one of the sources of microplastics emissions into the aquatic environment. Investigating the actual status of microplastic emissions from the wastewater treatment facilities we supply will be necessary to address the microplastic problem in the future. We surveyed six water treatment facilities in Japan and one overseas demonstration facility, and report the results here.
The concentration of microplastics in raw water varied greatly by facility type, with higher concentrations in raw water from recycling facilities that handle plastic products and sludge treatment centers with high concentrations of solids in raw water. In terms of microplastic removal performance for individual treatment processes, sand filtration and fiber filtration were highly effective, with only a few microplastics per cubic meter of treated water. The effect on the treated water of fibers detaching from the fiber media was considered to be small.
- Lead author
- Yuji Miyazaki
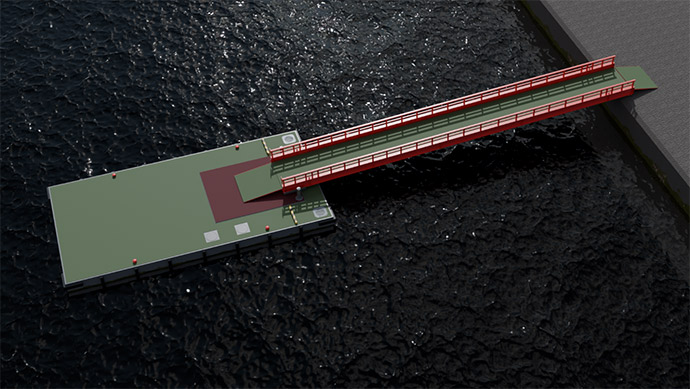
Since 2021, Kanadevia Corporation has been developing a new type of steel floating pier (hereinafter referred to as “steel floating pier”) for motion reduction in conjunction with Fukken Co., Ltd. The method of motion reduction involves adjusting the position of weights installed inside the floating pier to avoid resonance between the waves and the floating pier motions, thereby reducing the motions of the pier. First, the basic design of the steel floating pier was carried out to determine its main specifications, including its dimensions and inertia radius, as well as to verify stress levels and local strength for each member. This confirmed that the design specifications were satisfied. Next, numerical simulations based on the obtained main specifications were conducted to understand the trends seen in the motion responses of the steel floating pier. In addition, the coupled motion of the steel floating pier and the connecting bridge was confirmed through tank experiments, and it was found that the influence of the connecting bridge can significantly reduce the motion response of the steel floating pier. This paper presents the results of the basic design, numerical simulations, and water tank experiments for a steel floating pier.
- Lead author
- Kaichi Takeuchi
- Joint author
- Hideyuki Niizato, Yudai Mochiku, Susumu Matsuno,
(Fukken Co., Ltd) Koichi Minamimoto, Kazuyuki Yasumoto, Yukine Nakao

Kanadevia Corporation and Seiko Epson Corporation have developed a frequency-changing vibration sensor with an internal twin diapason-type oscillator based on Seiko Epson’s QMEMS and digital IP core technology. It achieved high resolution, low noise density, and wide bandwidth performance that surpass the conventional seismic servo-based and capacitive types. In order to use the vibration sensor for three-dimensional dynamic analysis of machines, we arranged its single axis sensors in three directions along the orthogonal XYZ axes and confirmed it offered sufficient accuracy in three-axis synchronization for ordinary rotating machines.
Predictive maintenance methods based on condition diagnosis are increasingly recognized as low cost and effective methods for maintaining industrial machinery and social infrastructure. Therefore, we used the three-dimensional vibration sensor thus developed to devise a method of expressing the shaft vibration of rotating machine, as an example, as a three-dimensional Lissajous figure, and explored its applicability to condition diagnosis. Our results confirm that this vibration sensor has sufficient performance to draw three-dimensional Lissajous figures, and that the basic vibration components of the machine could be drawn as Lissajous figures by applying appropriate pre-processing. Furthermore, when this vibration sensor was used to measure the vibration of actual rotating machinery, it was possible to detect changes due to aging in this machinery. In the future, we plan to compile more data and use the sensor as a failure prognosis function in comprehensive diagnostic systems being developed separately at Kanadevia Corporation.
- Lead author
- Toshio Takiya
- Joint author
- Keisuke Hata, Ryota Yoshiki,
(Seiko Epson Corporation) Kenta Sato, Masayoshi Todorokihara, Yasushi Yoshikawa, Masayuki Oto
[Short report]
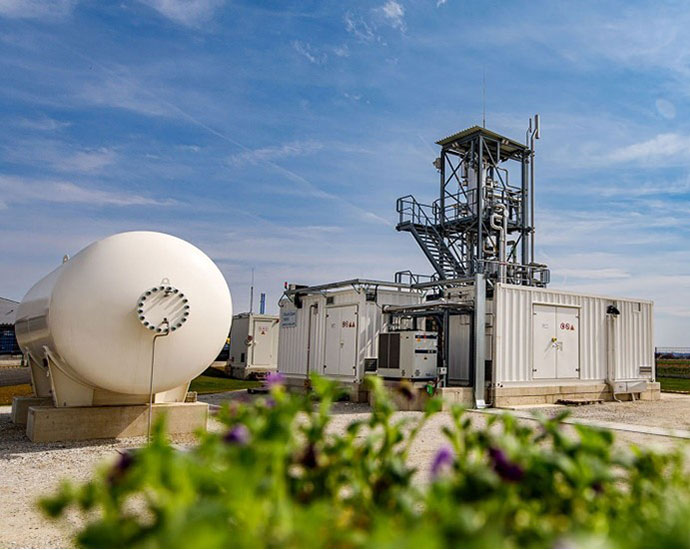

Kanadevia Inova AG (Inova) has developed a proprietary biogas (or CO2) methanation reactor. The first example of the technology was brought to operation in 2022 in Gabersdorf (Austria). The technology allows converting H2 and biogas into substitute natural gas, which can be directly injected in the natural gas grid.
The technology represents a significant advancement in the transition towards excluding fossil carbon from natural gas grids. It plays a crucial role in integrating proprietary technologies, such as anaerobic digestion and water electrolysis, into a comprehensive net-zero strategy.
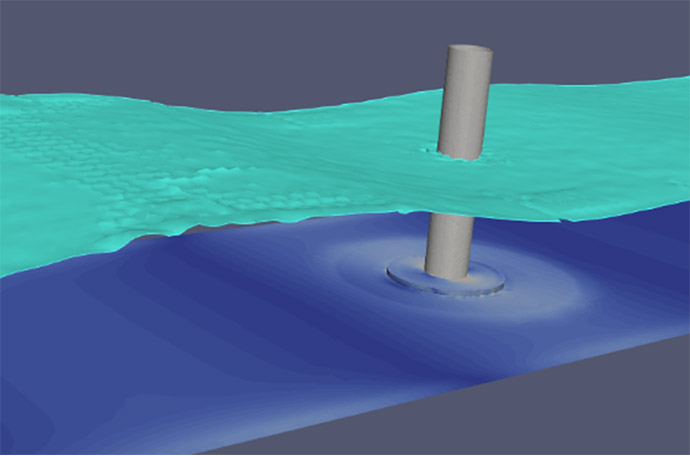
Plans for large-scale offshore wind farms are progressing in many countries, with the continued adoption of bottom-mounted wind turbines expected for the time being. The manufacturing and installation costs of foundation structures are estimated to account for approximately 20% of the capital cost of bottom-mounted offshore wind turbines, highlighting the need for further cost reductions are expected.
This scour analysis is one of the technologies that contribute to cost reduction in the foundation structures of bottom-mounted offshore wind turbines. By integrating computational fluid dynamics with optimization calculations, the analysis enables the evaluation of scour patterns around foundation structures in a relatively short time. Scour, caused by the transport of seabed materials due to waves and currents, has traditionally been challenging to estimate through simple calculations. This document provides an overview of this analysis technology.
- Keywords
- computational fluid dynamics, scour,
bottom-mounted offshore wind turbines,
suction foundation, monopile foundation
Click here for inquiries about Kanadevia technology
