Climate Change (Disclosure based on TCFD Recommendations)
Basic Policy
We have designated carbon neutrality as one of Pillars of Success (Materialities), and we are committed to addressing climate change.
Disclosure based on TCFD Recommendations
In March 2021, we endorsed the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and in line with TCFD Recommendations, we will promote proactive disclosure of information with awareness of stakeholder requests.
Governance
The Kanadevia Group positions climate change as an important management issue.
Climate change-related initiatives are carried out by the Sustainability Promotion Committee, a subordinate body of the Board of Directors, and three subordinate committees, which deliberate on management policies and business activity policies and strategies related to carbon neutrality, and receive reports on the implementation status of various measures. Specific business strategies are implemented based on deliberations and decisions by the Management Strategy Committee and the Sustainability Promotion Committee.
For details, please refer to Sustainable Management Promotion System.
Third-party Opinion
We solicated opinions and advice from outside experts on the Group's efforts to address sustainability issues, including climate change, and reflect them in our Sustainability Promotion activities. In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023, we sought opinions on our Sustainability Promotion Project. For details, please refer to the Sustainability Section.
Strategy
Scenario Analysis
<Scenario Analysis Policy and Process>
In March 2021, we conducted climate change scenario analyses as recommended by the TCFD, selected climate change risks and opportunities, and conducted a qualitative assessment of financial impacts.
<Selected Scenarios, Target Businesses, Target Year>
Our analysis is divided into short-, medium-, and long-term time horizons, covering the period from the present to 2050, using 4℃, 2℃, and 1.5℃ scenarios.
| Key scenarios | Transition risks and opportunities: NZE, SDS, STEPS by IEA Physical risks and opportunities: RCP 1.9, 2.6, and 8.5 by IPCC |
|---|---|
| Target Businesses | WtE business, biogas plant business, wind power generation business |
| Target year | 2050 |
NZE: Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario
SDS: Sustainable Development Scenario
STEPS: Stated Policies Scenario
IPCC: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
RCP: Representative Concentration Pathways
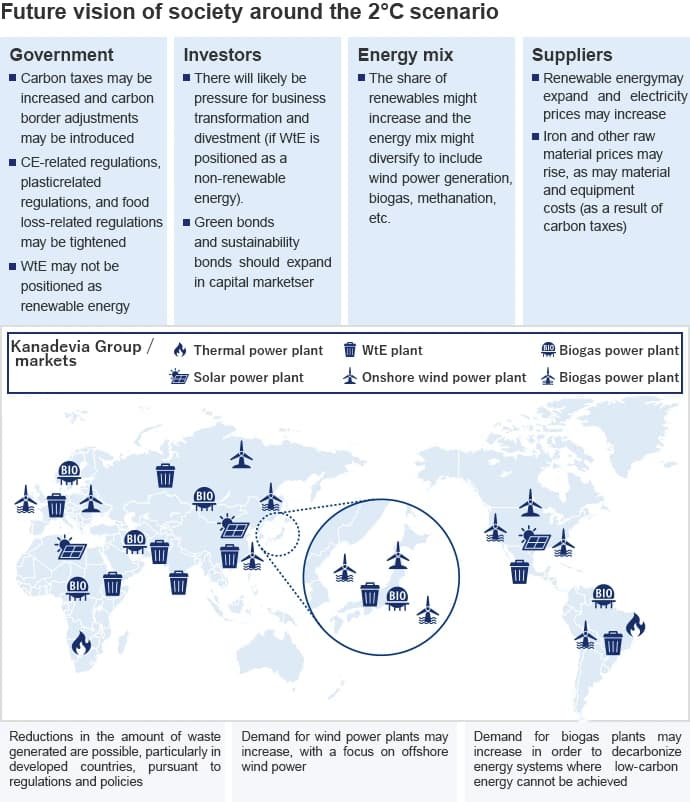
<Future vision of society around the 2℃ scenario>
In the 2℃ scenario, policies are developed to spread the use of renewable energy and curb greenhouse gas emissions, and there are impacts from rising costs due to higher raw material prices and carbon taxes. Meanwhile, as the share of renewables in the overall energy mix increases, demand for biogas and offshore wind power plants is expected to increase in addition to WtE plants. In particular, demand for waste treatment in developing countries is expected to grow. Although it will be necessary to monitor regulations in each region as needed, we will advance R&D to generate technical innovations to achieve sustainable growth, keeping in mind the possibility that the amount of waste generated in developed countries will decrease and that the growth in demand for waste treatment will decline.
| Item | Anticipated changes and worldview |
Financial impact |
Countermeasures |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Overview |
Scenario | |||||||
| 4℃ | 2℃ | 1.5℃ | ||||||
| Transition | Risks | Introduction of carbon taxes |
Operation costs increase as a result of carbon pricing If carbon border adjustments are implemented, costs associated with importing and exporting materials and equipment may increase |
High | High |
|
||
| Higher raw material costs |
Procurement costs for energy-intensive materials and equipment rise (items that use iron, copper, cement, plastic, etc. as raw materials) |
Medium | Medium |
|
||||
| Risks and opportunities | Changes in policies, regulations, and energy mix | WtE plants |
Share of renewable energy varies widely by scenario (WtE plants) Regulations on circular economy, plastics, and food losses are strengthened and waste processing volumes decrease to limit temperature rise WtE is no longer treated as renewable energy in developed countries and demand for new plant stagnates Overseas markets expand substantially as a solution to increased waste generation and landfill problems associated with economic growth in developing countries (Biogas and wind power plants) Markets expand significantly in low-carbon societies (particularly for offshore wind power) |
High | Medium |
|
||
| Biogas plants | High | Medium | ||||||
| Wind power plants | Medium | |||||||
| Physical | Risks and opportunities | Worsening natural disasters (floods, lightning strikes, etc.) |
Natural disasters, such as floods, typhoons, heavy rain, and lightning strikes, damage plants, resulting in additional costs to restore plants and reduced revenues during downtime for DBO projects Orders for repair work on damaged facilities increase |
High |
|
|||
Setting the Pillars of Success (Materialities)
The results of the scenario analysis are reflected in the Medium-Term Management Plan, as well as confirmed and reviewed by the Sustainability Promotion Project, and reflected in the recognition of social issues that form the background for setting the “Pillars of Success,” analysis of risks and opportunities related to the “Pillars of Success,” measures and roadmaps.In order to appropriately incorporate changes in the external environment, needs, and expectations into the Medium-Term Management Plan and other business plans, the “Pillars of Success” will be reviewed every three to five years. The scenario analysis will be reviewed at the same time in order to appropriately capture changes in the external environment.
Indicators and Targets
| FY2025 | FY2030 | FY2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1,2 | 34% reduction compared to FY2013 | - | - |
| Scope1,2,3 | - | 50% reduction compared to FY2013 | Carbon neutrality |
Track Records
Scope3
FY2022 estimate 33,078kt-CO2e
[Main categories]
Category 11 (Use of products sold) 31,839kt-CO2e
Category 1 (Products and services purchased) 1,142kt-CO2e
Scope1,2
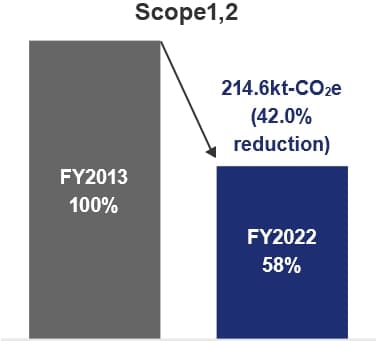
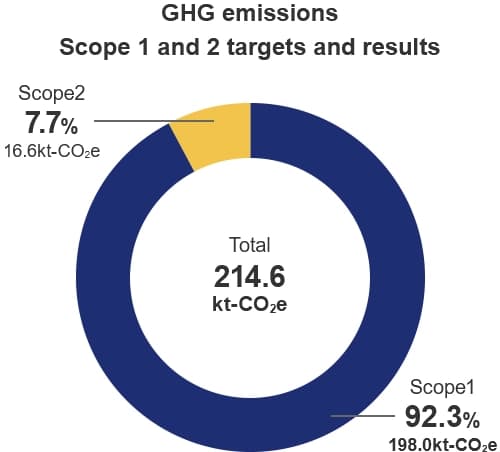
GHG emissions for Scope 1 and 2 were 214.6 kt-CO2e, a 42.0% decrease from the base year, due to a decrease in LNG input resulting from a decrease in demand in the power sales business and promotion of the introduction of green electricity.
Scope3
GHG emissions in the supply chain were 33,078 kt-CO2e (estimated for FY2023). Category 11 (use of products sold) had the highest emissions at 31,839 kt-CO2e, which are primarily life cycle emissions from marine engines.
Climate Change and Risk Management
Policies related to climate change in each country and region have significant impacts on the profitability and sustainability of each of our businesses. The Kanadevia Group has conducted scenario analysis for businesses that are likely to be affected by climate change using multiple climate change scenarios such as those from the IEA (International Energy Agency). Subsequently, we analyzed the impacts from both risks and opportunity perspectives and formulated Pillars of Success (Materialities).
In the future, we will establish a system to determine the materiality of risks based on quantitative and qualitative criteria, and to decide whether to promote or not and how to respond to such risks in deliberations by the Board of Directors and the Management Committee, and in decisions by the Representative Directors.
Initiatives
Manufacturing Processes
We will promote our own fuel conversion, increase energy self-sufficiency, and install energy-saving equipment to reduce Scope 1 and 2 to net-zero.
- Scope 1 and 2 50% reduction from FY2013
- Promotion of fuel conversion for marine engine commissioning fuel
- Promote switchover to renewable energy (facility switchover)
- Promote decarbonization by introducing in-house power generation and utilizing in-house technologies
- Promotion of power leveling by using large storage batteries
- Switchover to renewable energy (facility switchover) completed

- Promote switchover to renewable energy (facility switchover)
- Systematic renewal of transformers, air conditioning equipment, etc., to optimize layout and promote space saving
Scope3 compatible
We will work to reduce GHG emissions throughout the product lifecycle, and encourage contract manufacturers and suppliers to reduce their emissions as well.
- Scope 3 data disclosure started
- Started to consider reduction measures
- Scope 1,2,3 Carbon neutral

- Established Scope 3 calculation logic, estimated calculation for FY2022, and started considering countermeasures
- Implement SAQ for suppliers
